Creasol DomBusTH - Dispositivo Domoticz com sensores de temperatura e umidade, 4 entradas, 2 saídas, 3 LEDs
- Em promoção!
- -25%
Email: store@creasol.it - Telegram: CreasolTech - Whatsapp: +393283730010
Correio prioritário: rápido e barato - Express Courie
Contate-nos antes de devolver produtos!

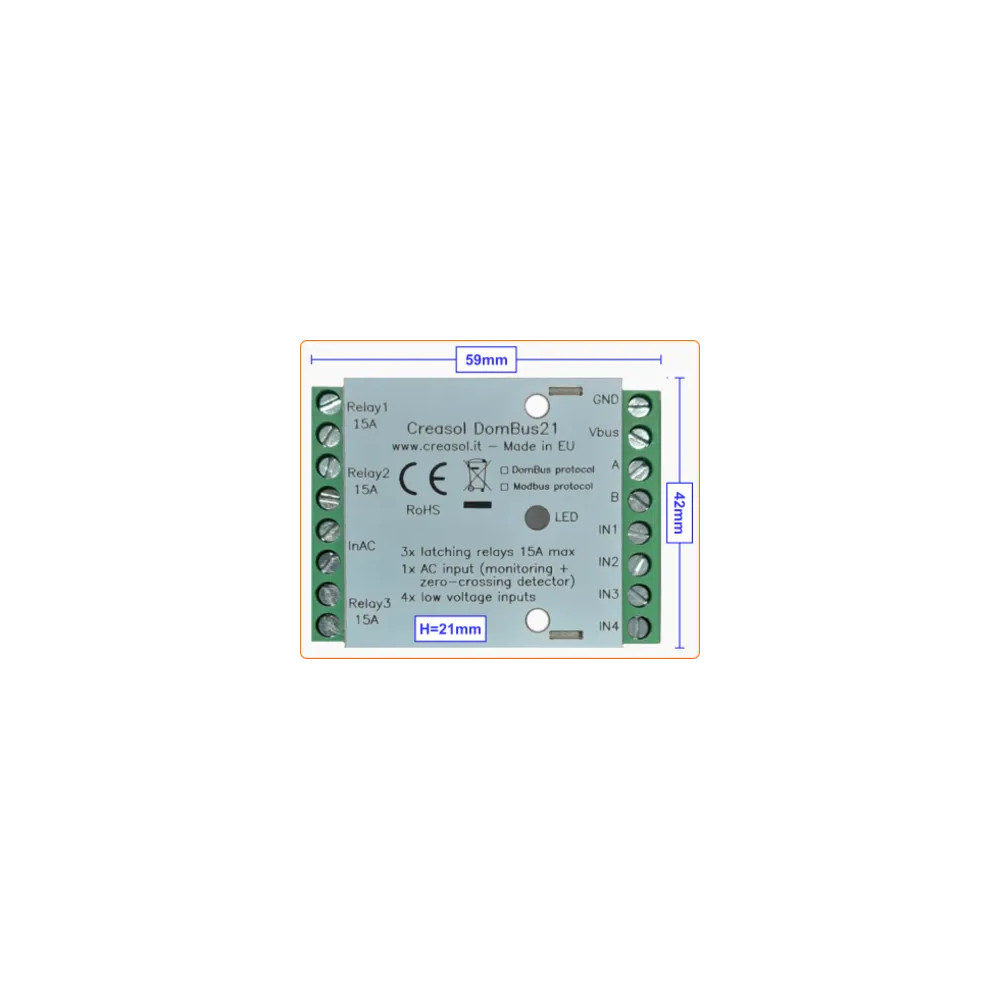
Muito compacto e com baixo consumo de energia módulo com 3 relés de 15A, 1 entrada CA, 4 entradas analógicas/digitais.
 Suporte total: a maioria dos produtos são projetados por nós!
Suporte total: a maioria dos produtos são projetados por nós!
Email: store@creasol.it - Telegram: CreasolTech - Whatsapp: +393283730010
 Os pedidos são enviados em até 1 dia útil
Os pedidos são enviados em até 1 dia útil
Correio prioritário: rápido e barato - Express Courie
 24 meses de garantia, fácil devolução/reembolso
24 meses de garantia, fácil devolução/reembolso
Contate-nos antes de devolver produtos!
Módulo domótico confiável de baixo consumo projetado para habilitar/desabilitar cargas economizando consumo de energia, zerando a energia em espera.
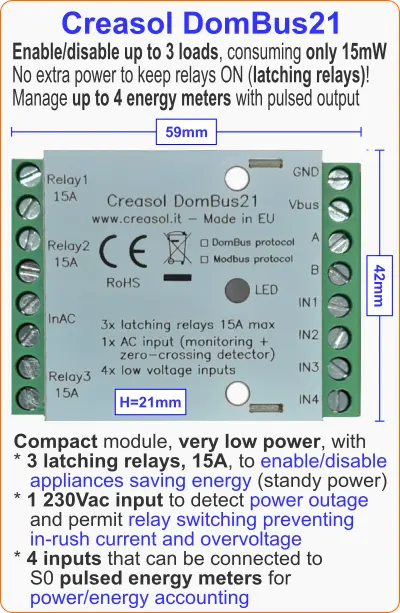 Ele usa 3 relés de travamento, 15A 250Vac, que não consome nada quando está ativo, podendo ser utilizado para habilitar cargas ou geradores de até 3kW que estão OFF por muito tempo. Além disso, desligar a energia das cargas durante tempestades com raios ajuda a evitar danos causados por descargas eletrostáticas.
Ele usa 3 relés de travamento, 15A 250Vac, que não consome nada quando está ativo, podendo ser utilizado para habilitar cargas ou geradores de até 3kW que estão OFF por muito tempo. Além disso, desligar a energia das cargas durante tempestades com raios ajuda a evitar danos causados por descargas eletrostáticas.
Ele também tem 1 entrada CA para detectar tensão de 230 Vca (detectando queda de energia), que também atua como um detector de cruzamento por zero que permite habilitar relés quando a tensão é zero (para minimizar a corrente de pico, no caso de cargas capacitivas) e desabilitar relés quando a corrente estiver em zero (para minimizar a sobretensão em caso de cargas indutivas).
4 entradas de baixa tensão, que pode ser configurado como analógico ou digital, permite conectar interruptores de botão de pressão, sondas térmicas NTC, sensores de alarme e contadores de energia/gás/água com saída pulsada.
Os 3 relés de travamento podem ser usados para habilitar/desabilitar:
Endereço padrão: 0xff21
| Porta# | Nome | Capacidades | Configuração padrão | Descrição |
| 1 | RL1 | FORA_DIGITAL | FORA_DIGITAL | Relé de travamento SPST 15A: a bobina é ativada somente durante as transições liga/desliga, não consumindo nada quando o relé está LIGADO ou DESLIGADO. A entrada INAC deve ser conectada a 230 Vca para permitir a detecção de cruzamento por zero, evitando alta corrente de pico (para cargas capacitivas) e sobretensão (para cargas indutivas) |
| 2 | RL2 | FORA_DIGITAL | FORA_DIGITAL | Relé de travamento SPST 15A: a bobina é ativada apenas durante as transições liga/desliga, não consumindo nada quandoo relé está LIGADO ou DESLIGADO. A entrada INAC deve ser conectada a 230 Vca para permitir a detecção de cruzamento por zero, evitando alta corrente de pico (para cargas capacitivas) e sobretensão (para cargas indutivas) |
| 3 | RL3 | FORA_DIGITAL | FORA_DIGITAL | Relé de travamento SPST 15A: a bobina é ativada somente durante as transições liga/desliga, não consumindo nada quando o relé está LIGADO ou DESLIGADO. A entrada INAC deve ser conectada a 230 Vca para permitir a detecção de cruzamento por zero, evitando alta corrente de pico (para cargas capacitivas) e sobretensão (para cargas indutivas) |
| 4 | INAC | EM_AC, EM_CONTADOR | EM_AC | Entrada optoisolada, que pode ser conectada a um disjuntor (para notificar quedas de energia, especialmente para geladeiras e bombas de calor), PIRs com saída de 230 V (para monitorar presença), luz e aparelhos (para monitorar quando a luz ou os dispositivos estão LIGADOS)./td> |
| 5 | IN1 | EM_DIGITAL, EUN_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN, EM_ANALOG, EM_TWINBUTTON, EM_COUNTER | EM_DIGITAL | Entrada analógica ou digital, com pullup opcional de 10k (jumper pcb) e pulldown interno opcional (ativado quando configurado como IN_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN). O bloco de terminais comum é GND: botão de pressão, interruptor, botão duplo (botão duplo com resistor de 10k entre os botões), sensor de alarme, termistor NTC de 10k, contador com saída pulsada (medidor de energia, medidor de gás, medidor de vazão de água), ... devem ser conectados a esta entrada e ao GND. |
| 6 | IN2 | EM_DIGITAL, EM_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN, EM_ANALOG, EM_TWINBUTTON, EM_COUNTER | EM_DIGITAL | Entrada analógica ou digital, com pullup opcional de 10k (jumper pcb) e pulldown interno opcional (ativado quando configurado como IN_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN). O bloco de terminais comum é GND: botão de pressão, interruptor, botão duplo (botão duplo com resistor de 10k entre os botões), sensor de alarme, termistor NTC de 10k, contador com saída pulsada (medidor de energia, medidor de gás, medidor de vazão de água), ... devem ser conectados a esta entrada e ao GND. |
| 7 | IN3 | EM_DIGITAL, EM_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN, EM_ANALOGO, EM_CONTADOR | EM_DIGITAL | Entrada analógica ou digital, com pullup ou pulldown interno (ativado quando configurado como IN_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN). O bloco de terminais comum é GND: botão de pressão, interruptor, sensor de alarme, contador com saída pulsada (medidor de energia, medidor de gás, medidor de vazão de água), ... devem ser conectados a esta entrada e ao GND. |
| 8 | IN4 | EM_DIGITAL, EM_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN, EM_ANALOGO, EM_CONTADOR | EM_DIGITAL | Entrada analógica ou digital, com pullup ou pulldown interno (ativado quando configurado como IN_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN). O bloco de terminais comum é GND: botão de pressão, interruptor, sensor de alarme, contador com saída pulsada (medidor de energia, medidor de gás, medidor de vazão de água), ... devem ser conectados a esta entrada e ao GND. |
Ao ligar, o módulo mostra no LED vermelho o endereço atual do escravo Modbus (endereço de registro = 8192) em formato decimal, no LED verde a taxa de transmissão serial (reg. 8193) e, finalmente, no LED vermelho a paridade serial (reg. 8194).
Se um valor for zero, um flash longo será emitido.
Por exemplo,se reg(8192)=33, reg(8193)=0, reg(8194)=0, na alimentação serão mostrados os seguintes flashes de led:
3 flashes vermelhos, pausa, 3 flashes vermelhos (endereço escravo = 0x21 = 33 decimal), pausa, 1 flash verde longo (reg(8193)=0 => taxa de transmissão=115200bps), pausa, 1 flash vermelho longo (reg(8194)=0 => paridade=Nenhuma).
O dispositivo estará operacional somente quando os parâmetros de endereço/taxa de transmissão/paridade forem exibidos: então o módulo aceitará comandos do Modbus RTU e exibirá periodicamente o status de saída para todas as portas, de 1 até a porta máxima: o flash verde significa que o status da porta está Desligado, o flash vermelho significa que a porta está Ligada.
Endereço escravo padrão: 33 (0x21)
| Endereço | Nome | Valores | Descrição |
| 0 | RL1 | 0=DESLIGADO, 1 ou 65280=LIGADO, 2-65279=LIGADO para o tempo especificado. A lógica pode ser invertida especificando a opção INVERTED (no endereço 512+porta) |
Relé de travamento SPST 15A: a bobina é ativada somente durante as transições liga/desliga, não consumindo nada quando o relé está LIGADO ou DESLIGADO. A entrada INAC deve ser conectada a 230 Vca para permitir a detecção de cruzamento por zero, evitando altas tensões.corrente de pico (para cargas capacitivas) e sobretensão (para cargas indutivas) |
| 1 | RL2 | 0=DESLIGADO, 1 ou 65280=LIGADO, 2-65279=LIGADO para o tempo especificado. A lógica pode ser invertida especificando a opção INVERTED (no endereço 512+porta) |
Relé de travamento SPST 15A: a bobina é ativada somente durante as transições liga/desliga, não consumindo nada quando o relé está LIGADO ou DESLIGADO. A entrada INAC deve ser conectada a 230 Vca para permitir a detecção de cruzamento por zero, evitando alta corrente de pico (para cargas capacitivas) e sobretensão (para cargas indutivas) |
| 2 | RL3 | 0=DESLIGADO, 1 ou 65280=LIGADO, 2-65279=LIGADO para o tempo especificado. A lógica pode ser invertida especificando a opção INVERTED (no endereço 512+porta) |
Relé de travamento SPST 15A: a bobina é ativada somente durante as transições liga/desliga, não consumindo nada quando o relé está LIGADO ou DESLIGADO. A entrada INAC deve ser conectada a 230 Vca para permitir a detecção de cruzamento por zero, evitando alta corrente de pico (para cargas capacitivas) e sobretensão (para cargas indutivas) |
| 3 | INAC | 0=OFF (flutuante), 1=ON (sinal de 100-250 V detectado) | Entrada optoisolada, que pode ser conectada a um disjuntor (para notificar quedas de energia, especialmente para geladeiras e bombas de calor), PIRs com saída de 230 V (para monitorar presença), luz e aparelhos (para monitorar quando a luz ou os dispositivos estão LIGADOS)./td> |
| 4 | IN1 | 0=DESLIGADO, 1=LIGADO ou 0-65535 se a porta estiver configurada como analógica. Veja abaixo mais informações. |
Entrada analógica ou digital, com pullup opcional de 10k (jumper pcb) e pulldown interno opcional (ativado quando configurado como IN_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN). O bloco de terminais comum é GND: botão de pressão, interruptor, botão duplo (botão duplo com resistor de 10k entre os botões), sensor de alarme, termistor NTC de 10k, contador com saída pulsada (medidor de energia, medidor de gás, medidor de vazão de água), ... devem ser conectados a esta entrada e ao GND. |
| 5 | IN2 | 0=DESLIGADO, 1=LIGADO ou 0-65535 se a porta estiver configurada como analógica. Veja abaixo mais informações. |
Entrada analógica ou digital, com pullup opcional de 10k (jumper pcb)e pulldown interno opcional (ativado quando configurado como IN_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN). O bloco de terminais comum é GND: botão de pressão, interruptor, botão duplo (botão duplo com resistor de 10k entre os botões), sensor de alarme, termistor NTC de 10k, contador com saída pulsada (medidor de energia, medidor de gás, medidor de vazão de água), ... devem ser conectados a esta entrada e ao GND. |
| 6 | IN3 | 0=DESLIGADO, 1=LIGADO ou 0-65535 se a porta estiver configurada como analógica. Veja abaixo mais informações. |
Entrada analógica ou digital, com pullup ou pulldown interno (ativado quando configurado como IN_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN). O bloco de terminais comum é GND: botão de pressão, interruptor, sensor de alarme, contador com saída pulsada (medidor de energia, medidor de gás, medidor de vazão de água), ... devem ser conectados a esta entrada e ao GND. |
| 7 | IN4 | 0=DESLIGADO, 1=LIGADO ou 0-65535 se a porta estiver configurada como analógica. Veja abaixo mais informações. |
Entrada analógica ou digital, com pullup ou pulldown interno (ativado quando configurado como IN_DIGITAL_PULLDOWN). O bloco de terminais comum é GND: botão de pressão, interruptor, sensor de alarme, contador com pulsosaída (medidor de energia, medidor de gás, medidor de vazão de água), ... deve ser conectado a esta entrada e ao GND. |
| 256-273 | Configuração da porta | 1=FORA_DIGITAL, 2=SAÍDA_RELÉ_LP, ... |
Comando usado para configurar a porta 1 (256), porta 2 (257), ... como OUT_DIGITAL ou OUT_RELAY_LP (relé de baixo consumo de energia) ou outro valor (veja a tabela abaixo) |
| 512-529 | Opção de porta | 0=NORMAL, 1=INVERTED (saída normalmente ON, ou entrada está ON quando a tensão da porta é 0 V) | Definir opção de porta. Se definido como 1, a saída permanece LIGADA após a inicialização até que a porta seja confirmada (então os relés são DESLIGADOS). Para entradas, definindo INVERTED o valor da porta é LIGADO (1) quando a tensão de entrada é 0 V, DESLIGADO quando a entrada é deixada aberta com pullhigh interno habilitado. |
| 8192 | Endereço do escravo | 1-247 | Permite alterar o endereço escravo do módulo, sendo possível adicionar outros módulos ao mesmomesmo ônibus |
| 8193 | Taxa de bits serial | 0=115200bps, 1=57600, 2=38400, 3=19200, 4=9600, 5=4800, 6=2400, 7=1200bps | Velocidade serial, padrão 115200 bps 8,n,1 |
| 8194 | Paridade serial | 0=Nenhum, 1=Par, 2=Ímpar | Paridade serial, padrão nenhum (115200 bps 8,n,1) |
| 8198 | Revisão, principal | Somente leitura | Obter versão do firmware, número principal. Por exemplo, "02" significa que a revisão é "02XX", onde XX é definido pelo parâmetro 8199 |
| 8199 | Revisão, menor | Somente leitura | Obter versão do firmware, número secundário. Por exemplo, "h1" significa que a revisão é "XXh1", onde XX é definido pelo parâmetro 8198 |
É possível ativar uma ou mais saídas parara certa quantidade de tempo (saída monoestável/temporizador) conforme indicado na tabela. O parâmetro correspondente ao tempo necessário pode ser computado usando as seguintes regras:
De 0 a 60s => 31,25ms resolução 2=62,5ms, 3=93,75ms, ... 1920=60s => valor=tempo_em_milissegundos/31,5
De 1m a 1h com resolução de 1s 1921=61s, 3540+1920=5460=1h => valor=(tempo_em_segundos-60)+1920
De 1h a 1d com resolução de 1m 5461=1h+1m, 1380+5460=6840=24h => valor=(tempo_em_minutos-60)+5460
De 1d a 1500 dias com resolução de 1h 6841=25h, 6842=26h, e assim por diante => valor=(tempo_em_horas-24)+6840
As tabelas a seguir mostram alguns exemplos de comandos Modbus.
| Endereço Escravo | Código de função | Endereço Reg. | Valor Reg. | Quadro | Descrição |
| 55 | 06 | 8192 | 1 | [37][06][20][00][00][01][xx][xx] | Alterar endereço do escravo de 54 (0x36) para 1 |
| 01 | 06 | 8193 | 4 | [01][06][20][01][00][04][D2][09] | Defina a velocidade serial para 9600 bps |
| 01 | 06 | 8194 | 1 | [01][06][20][02][00][01][E2][0A] | Definir paridade uniforme |
| 49 | 10 | 8192 | 1,4,1 | [31][10][20][00][00][03][06][00][01][00][04][00][01][B1][71] | Com um único comando,defina o endereço do escravo para 1, velocidade serial para 9600bps, paridade par. O endereço do módulo original era 49 (0x31) neste exemplo. |
| 01 | 06 | 0 | 65280 | [01][06][00][00][FF][00][C8][3A] | Ativar saída RL1 para sempre (65280=0xff00) |
| 01 | 06 | 1 | 960 | [01][06][00][01][03][C0][D8][AA] | Ative RL2 por 960/32=30s |
| 01 | 06 | 255 | 0 | [01][06][00][FF][00][00][B9][FA] | Desabilitar todas as saídas (Reg.Addr=255) |
| 01 | 10 | 0 | 32,0,0,65280 | [31][10][00][00][00][04][08][00][20][00][00][00][00][FF][00][E6][5C ] | Defina RL1 como Ligado por 1s (32), RL2 Desligado, RL3 Desligado, RL4 Ligado - Máximo de 10 registradores podem ser definidos em um comando |
| 01 | 03 | 255 | 1 | [01][03][00][FF][00][01][B4][3A] | Lê um valor de 16 bits com status de portas. Por exemplo, se o valor retornado for 0xd1 (0b11010001), o status de saída é: RL8=Ligado, RL7=Ligado, RL6=Desligado, RL5=Ligado, RL4=Desligado, RL3=Desligado, RL2=Desligado, RL1=Ligado |
| 01 | 03 | 8198 | 2 | [01][03][20][06][00][02][2F][CA] | Leia 4 bytes dentro da versão do módulo. Por exemplo, se o valor retornado for <30><32><68><31> (em formato hexadecimal), o valor ASCII correspondente será "02h1" (Firmware 02h1) |
| 01 | 0F | 0 | 8,1,0xd1 | [01][0F][00][00][00][08][01][D1][3E][C9] | Defina o status da bobina como 0xd1 (0b11010001), ativando RL8, RL7, RL5, RL1 e desabilitando outros relés |
| 01 | 01 | 0 | 8 | [01][01][00][00][00][08][3D][CC] | Leia o status da bobina. Se o valor retornado for 0xd1 (0b11010001), significa que RL8, RL7, RL5 e RL1 estão ligados |
O protocolo Modbus pode ser testado facilmente usando um programa Modbus, como enquete mp para Linux:
mbpoll -v -m rtu -0 -1 -a1 -b115200 -Pnenhum -r 0 /dev/ttyUSB0 32 0 64 128 0 0 0 65280
para ativar RL1 por 1s, R3 por 2s, RL4 por 4s e RL8 para sempre.
mbpoll -v -m rtu -0 -1 -a1 -b115200 -Pnenhum -r 255 -c 1 /dev/ttyUSB0
para ler todos os estados das portas.
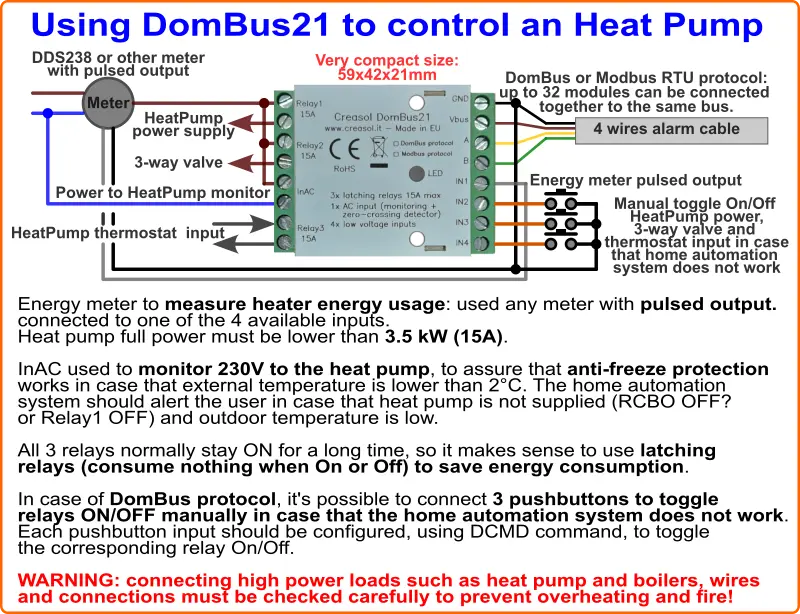
As bombas de calor podem ter um consumo de energia em espera de 5 W ou mais: elas permanecem ligadas por muito tempo, mas também permanecem desligadas por muito tempo, então faz sentido habilitar o fornecimento de energia da bomba de calor somente quando necessário.
O diagrama a seguir mostra como gerenciar a bomba de calor pelo módulo DomBus21, para obter os seguintes recursos em seu sistema de automação residencial:
O consumo de energia do DomBus21 é de cerca de 15mW mesmo com os relés ligados: considerando que a bomba de calor está ligada durante 66% do tempo, o a energia economizada é de cerca de 25 kWh/ano comparado a um sistema onde a bomba de calor está sempre ligada e usa módulos de relé de automação residencial ineficientes!
Também, ter a bomba de calor desconectada pode evitar danos por flutuações de tensão de 230 V ou descargas eletrostáticas.
Tenha cuidado com a fiação: DomBus21 lida com cargas com no máximo 15A (3,5kW), que podem superaquecer ou queimar se as conexões não forem feitas corretamente. Conexões de alta potência devem ser monitoradas com uma câmera térmica IR para garantir que não superaqueçam ao fornecer alta potência.
The following video shows a presentation of some domotic modules designed and produced in Italy by Creasol to make a reliable, easy and power-optimized home automation system.
The next video shows our Smart EVSE module that can be used to charge the electric car by using only solar power, or adding 25/50/75/100% of available power from the electrical grid.
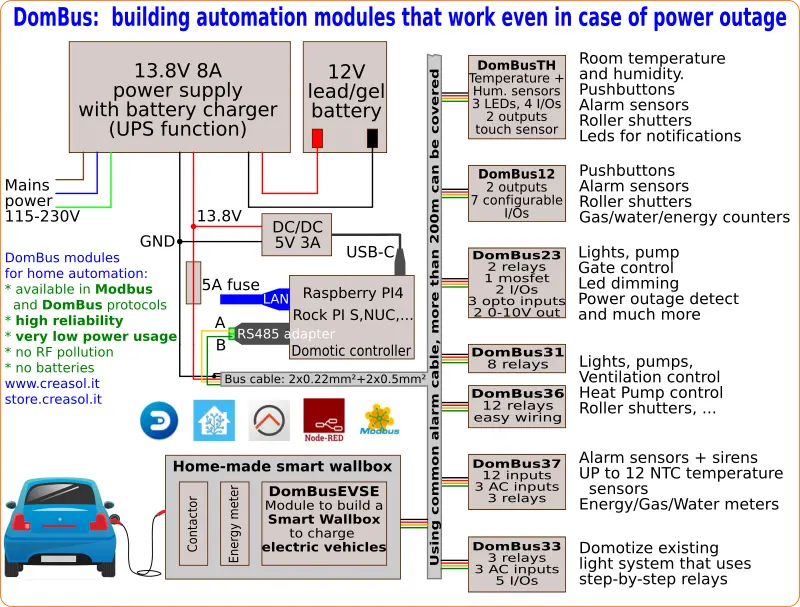
Our industrial and home automation modules are designed to be
Modules are available in two version:
Store website - Information website
For our products we can offer FULL SUPPORT and CUSTOMIZATION: please contact us by Email or Telegram
 Complete solution to make a Smart EVSE, charging the electric vehicle using only energy from renewable source (photovoltaic, wind, ...), or adding 25-50-75-100% of available power from the grid.
Complete solution to make a Smart EVSE, charging the electric vehicle using only energy from renewable source (photovoltaic, wind, ...), or adding 25-50-75-100% of available power from the grid.
 Compact board, 32x17mm, to be installed on blank cover with a 4mm hole in the middle, to exchange air for the relative humidity sensor. It can be installed in every room to monitor temperature and humidity, check alarm sensors, control blind motor UP/DOWN, send notifications (using red and green leds) and activate white led in case of power outage.
Compact board, 32x17mm, to be installed on blank cover with a 4mm hole in the middle, to exchange air for the relative humidity sensor. It can be installed in every room to monitor temperature and humidity, check alarm sensors, control blind motor UP/DOWN, send notifications (using red and green leds) and activate white led in case of power outage.
Includes:
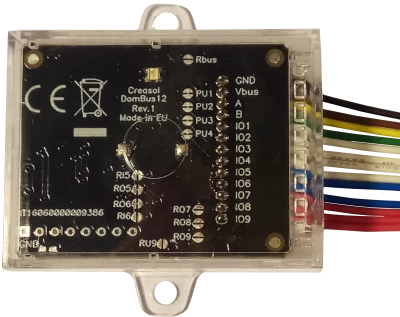 Very compact, versatile and cost-effective module with 9 ports. Each port can be configured by software as:
Very compact, versatile and cost-effective module with 9 ports. Each port can be configured by software as:
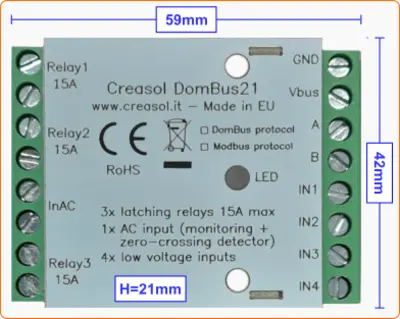 Very low power consumption module designed to enable up to 3 high power loads, up to 15A (3kW).
Very low power consumption module designed to enable up to 3 high power loads, up to 15A (3kW).
 Versatile module designed to control gate or garage door.
Versatile module designed to control gate or garage door.
 DIN rail low profile module, with 8 relays and very low power consumption:
DIN rail low profile module, with 8 relays and very low power consumption:
 Versatile module with 230V inputs and outputs, and 5 low voltage I/Os.
Versatile module with 230V inputs and outputs, and 5 low voltage I/Os.
 Module designed to control 3 lights already existing and actually controlled by 230V pushbuttons and step-by-step relays. In this way each light can be activated by existing pushbuttons, and by the domotic controller.
Module designed to control 3 lights already existing and actually controlled by 230V pushbuttons and step-by-step relays. In this way each light can be activated by existing pushbuttons, and by the domotic controller.
Each relay can toggle the existing step-relay, switching the light On/Off. The optoisolator monitors the light status. The 5 I/Os can be connected to pushbuttons to activate or deactivate one or all lights.
 DIN rail module, low profile, with 12 relays outputs and very low power consumption.
DIN rail module, low profile, with 12 relays outputs and very low power consumption.
 Module designed to be connected to alarm sensors (magnetc contact sensors, PIRs, tampers): it's able to monitor mains power supply (power outage / blackout) and also have 3 relays outputs.
Module designed to be connected to alarm sensors (magnetc contact sensors, PIRs, tampers): it's able to monitor mains power supply (power outage / blackout) and also have 3 relays outputs.
 DIN rail module designed for burglar alarm system.
DIN rail module designed for burglar alarm system.
![]() DIN rail module that control azimuth + elevation/tilt motors of a sun tracker, to maximize photovoltaic energy production during the day and seasons.
DIN rail module that control azimuth + elevation/tilt motors of a sun tracker, to maximize photovoltaic energy production during the day and seasons.
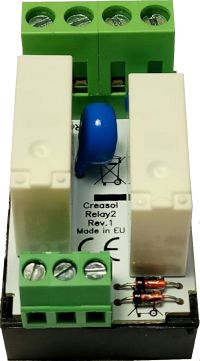 Simple module with 2 relays, to be used with DomBus modules or other electronic boards with open-collector or open-drain outputs
Simple module with 2 relays, to be used with DomBus modules or other electronic boards with open-collector or open-drain outputs
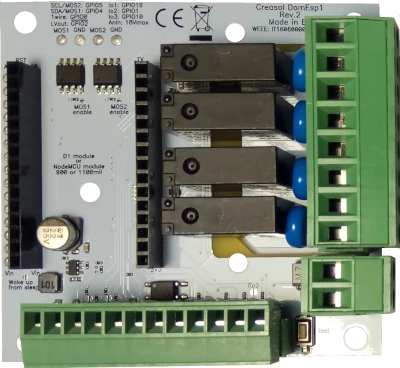 IoT board designed for NodeMCU v3 board using ESP8266 WiFi microcontroller
IoT board designed for NodeMCU v3 board using ESP8266 WiFi microcontroller